Minor planet 4 Vesta reaches opposition on 21 December 2023 when it can be found shining at mag. +6.6 among the stars of northern Orion.
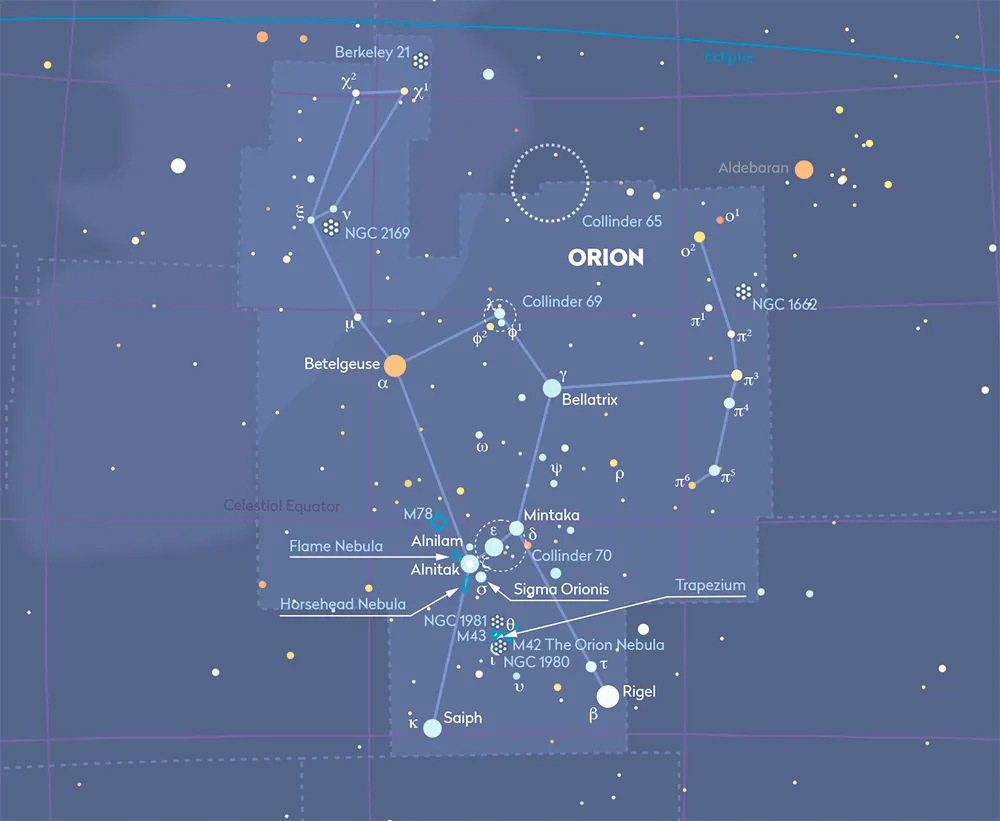
To fit within the IAU defined boundary of northern Orion is quite a feat, as this portion of the constellation, the bit north of his club and beneath the foot of the twin Castor in Gemini, is only 7.4° wide.
Vesta manages to stay within this boundary until 29 December when it slips slightly across the border into Taurus.
For regular stargazing advice, sign up to receive the BBC Sky at Night Magazine e-newsletter and listen to our regular Star Diary podcast.

Vesta begins December 2023 3.1° south-southwest of mag. +2.8 Tejat (Mu (μ) Geminorum).
From here it tracks west and slightly north to pass just north of mag. +5.8 68 Orionis on 8 and 9 December, mag. +4.6 Chi2 (χ2) Orionis on 16/17 December and mag. +4.4 Chi1 (χ1) Orionis on 24 and 25 December.
At the start of the month it appears at magnitude +7.2, brightening to +6.6 at opposition on 21 December before dimming slightly to +6.8 on New Year’s Eve.
This places Vesta squarely within range of binoculars and a small telescope is an ideal instrument to keep track of it.
Facts about Vesta
Vesta was discovered on 29 March 1807 by Wilhelm Olbers and was the fourth minor planet discovered.
You can find out more about this in our history of the astronomers known as the Celestial Police.
Vesta is a large object with a mean diameter of 525km. In the realm of the minor planets, only 1 Ceres is larger with an average diameter of 939km.
Under modern classification, 1 Ceres is a dwarf planet.
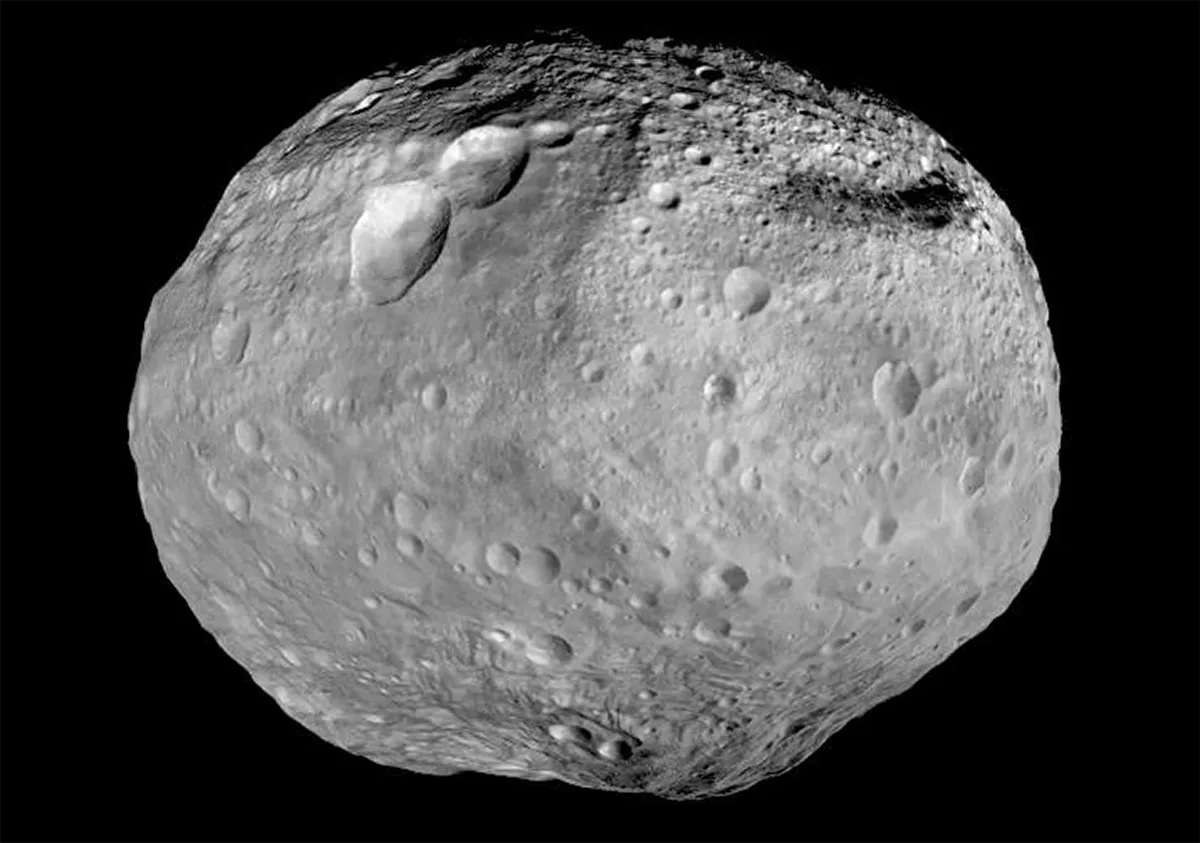

Vesta completes one orbit around the Sun every 3.63 years, its orbital path taking it out as far as 2.57 AU from the Sun and in as close as 2.15 AU.
During a poor opposition, Vesta may only reach mag. +8.5, but at a good opposition it may become a naked-eye object, shining at mag. +5.1.
Interestingly, its size combined with its varying distance from Earth means it presents an angular diameter which varies between 0.2 and 0.7 arcseconds.
This guide appeared in the December 2023 issue of BBC Sky at Night Magazine.


